Cademix Institute of Technology, Vienna, Austria | +43 650 967 7080 | info@cademix.org


Cademix Institute of Technology
Job seekers Portal for Career Acceleration, Continuing Education, European Job Market
Top Skills and Facilities Every Optometrist Should Know
By: Jom Johnson, Optometrist, Research Associate at Cademix Institute of Technology

Optometrists are the healthcare professionals who provide primary vision care. A well-known task of an Optometrist includes detailed history taking to prescribing glasses. The optoms take care of the primary complaints and findings of the patient. Afterwards they refer the patients to the ophthalmologist(doctor) for further diagnosis.
The purpose of optometry is to determine eyesight, to prescribe corrective lenses, and to diagnose eye disease. They are capable of detecting symptoms, prescribing medicines, and treating most eye diseases. They are healthcare professionals who provide primary vision services, which means there is a thorough history of prescription glasses.
Optoms are the most important part of the eye care system. They are experts in visual health monitoring and interpretation and are likely to spend full time with customers / patients in optical stores or hospitals. This gives every person great opportunities to suggest the “Right Vision Solution”, based on lifestyle and visual status. There are certain skills and techniques every optometrist should acquire to establish a good career in this field.
Communication with Patient
Communication abilities are among the most basic ability an optometrist can learn. One needs a good communication with the patient to conduct a perfect workup. Professionals say that the most basic step of treatment is understanding the patients need. Optometrists should understand the basic needs through proper communication with the patients.
Function in history-taking. Let’s talk about taking history.
The art of meticulous history taking involves:
- Demographic data – chief presenting complaints
- History of present illness – family history
History may vary from an adult to a child. The aforementioned illness tells us about the past of an adult. For an infant / toddler however, the history only includes the birth data and other rising chart.
The next skill we should have must be the proper knowledge about the workup. We must know what we are going to do. It must start from detailed history taking. He must be completely aware of the things he is asking. The history of every patient will be different for example the history of a child and an adult will be different. He must also be informed of what kind of questions to ask for the various groups.
THE EYE EXAMINATION
Human vision is the most important sense of all senses. The assessment of vision / visual evaluation is the crucial part of the function of an optometrist. We focus our discuss on the following essential functioning components of an optom.
- Vision assessment/ Taking of visual acuity
- External ocular examination
- Internal ocular examination / Fundus examination
- Visual field examination
The visual acuity
It is important to test both distance and near acuity [with / without glasses]. The Snellen test is widely used to test the central distance visual acuity, separately for each eye.

External ocular examination
This involves the examination of the head position, front and face alignment, eye brows, eyelids, lacrimal device, and eyeball using slit lamp examination.
Internal ocular examination
We use Slit lamp examination to study parts of the body such as conjunctiva, sclera (white part of the eye), cornea, anterior chamber, iris, pupil lens and posterior part or the fundus, where microscope used to examine a living tissue.
Fundus examination
It is necessary to diagnose the vitreous optic nerve head, retina and choroid using convex lenses or direct/indirect ophthalmoscope. Observation of the Fundus includes its media, optic disc, macula, retinal blood vessels and overall history.
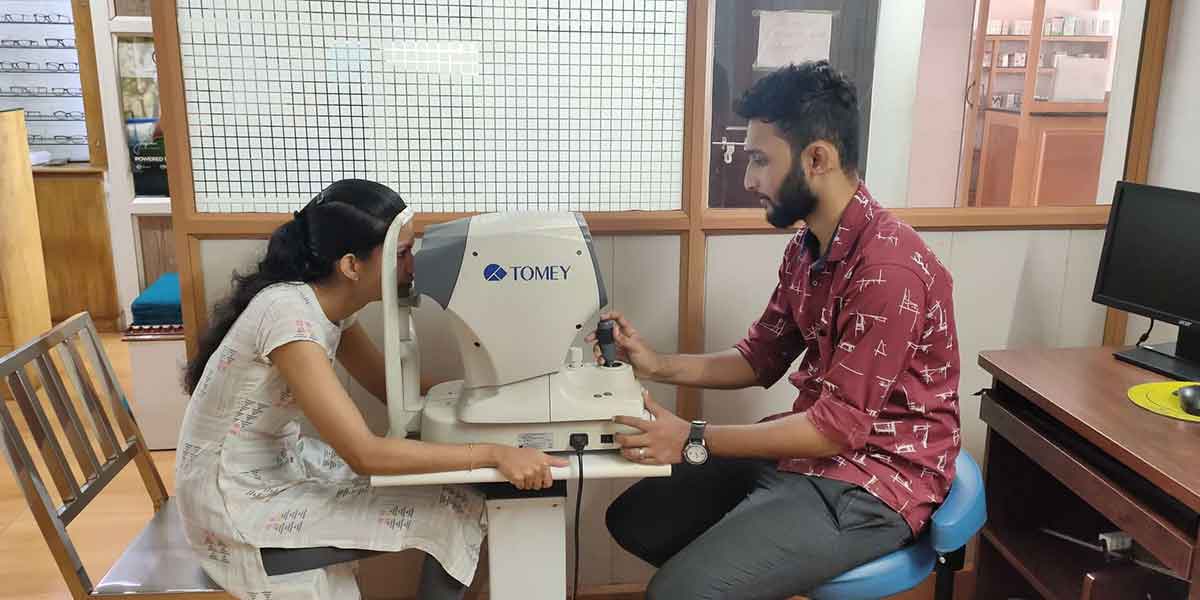
Visual field assessment
Evaluation of the visual field is important in many eye disorders. We use this technique to diagnose many eye conditions, such as glaucoma, optic disc disease, etc.
ENVISIONING THE OPTOMETRIC EXAMINATION
ROLE OF OPTOM BEYOND REFRACTION
Optometry is a primary eye care area which deals with the examination of the eye’s visual structures. In its primitive level, optometry was given a central focus on quantification and optical regulation of refractive errors. The historical timeline of this branch of medicine reflects a proud legacy where the discipline has made great strides through discovery, evolution and expansion. The vast field of modern optometry offers an endless opportunity to be a clinician, optician, science academic, educator or corporate professional, etc.
OCULAR MANAGEMENT BY AN OPTOMETRIST
A significant contribution to the clinical and community-based detection and treatment of refractive errors has been made by primary eye care specialists (a leading cause of visual impairment). By involving referral and co-management in their detection, it also plays a key role in alleviating numerous vision-threatening ocular disorders.
Optoms include a wide range of treatments, including vision and eye tests, screening, supervision, treatment of eye problems, prescription and availability of glass and contact lenses, low vision aids, and medicines.

Training of an Optometrist
Additional effort must be made to provide optometrists with thorough clinical training in order to play a part in the diagnosis of these blind eye diseases. The aim of this should be to train them well for a comprehensive ophthalmic examination, the handling of diagnostic equipment. Further, it follows by the examination and interpretation of clinical findings.
This helps in identifying the presence of any structural or functional damage in the visual system, the diagnosis of diseases. Afterwards, they should consider a proper referral as the responsibility of the optometrist to the community.
Skills we should have
After history taking we must be aware of the basic steps of eye examination which is the most imported part of workup. The steps may differ according to patient. The most important thing in eye examination will be the patients cooperation. Therefore, for a good cooperation there should be good communication maintained
A good optom is a personality who must be able to take quick decisions based on their findings. Therefore through a communication, he should be able to understand the do’s and dont’s in the workup. He must also be able to explain every procedure to the patient, before doing it. He must be able clarify patients doubts and worries.
Basic steps of examination starts from vision assessment and ends in slitlamp examination with fundus, vision assessment and followed by refraction to find out the power. Slitlamp examination helps to see anterior & posterior segment of the eye. Based on all these factors, we will decide what diagnostic tests should we do next.

Beyond the normal skill sets
An extraordinary expert in the area of optometry has wider range of skills than the technical skills mention above. The additional skills are those including added-value to the organizational, communication and Research and Development activities. Some of the major skills are
- Project Management or knowledge of agile project management
- Additive manufacturing and 3D printing
- Computer simulation and virtual experimentation
- Coordination of Research and development activities
Summary and Conclusion
Diagnostics helps to identify the abnormalities in the eye which cannot be see with the naked eye. Based on each finding we will decide what treatments should be given. There are different technologies available nowadays to see from cornea to retina of the eye. Thus we can make sure that there is no loop hole in our assessment.
Related Keywords:
Eye-care, Eye diseases, Eye-doctor, Glaucoma, Ocular, Eye exams, Eye exam, Eye health, Exams, Macular, Refractive, Astigmatism, Ophthalmology, Eye conditions, healthcare career
Retinal, Eye disease, Eyeglasses, Optometrist, Retina, Degeneration, Contact lenses, Contact-lens, Diabetic, Corneal, Ophthalmologist, Eye problems, Ophthalmic, Retinopathy, Optometry, Cataract, Eye surgery, jobs.
Cornea, Vision correction, Macular-degeneration, Cataracts, Vision loss, Blindness, Tech skills, Career Acceleration, Job vision, Age-related macular degeneration, Diabetic-retinopathy, Eyelid